The difference between two-phase and three-phase Hybrid Stepper Motors
 Mar 23, 2023|
Mar 23, 2023| View:228
View:228Due to their precise control and performance, Hybrid Stepper Motors are an integral part of many electromechanical systems. A key feature of a Hybrid Stepper Motor is its ability to operate in either a two-phase or three-phase configuration. The mode of operation of a stepper motor is determined by its internal wiring, rotor design, and the control signals applied to the motor. In this article, we will discuss the differences between two-phase and three-phase Stepper Motors, including performance, efficiency and cost.
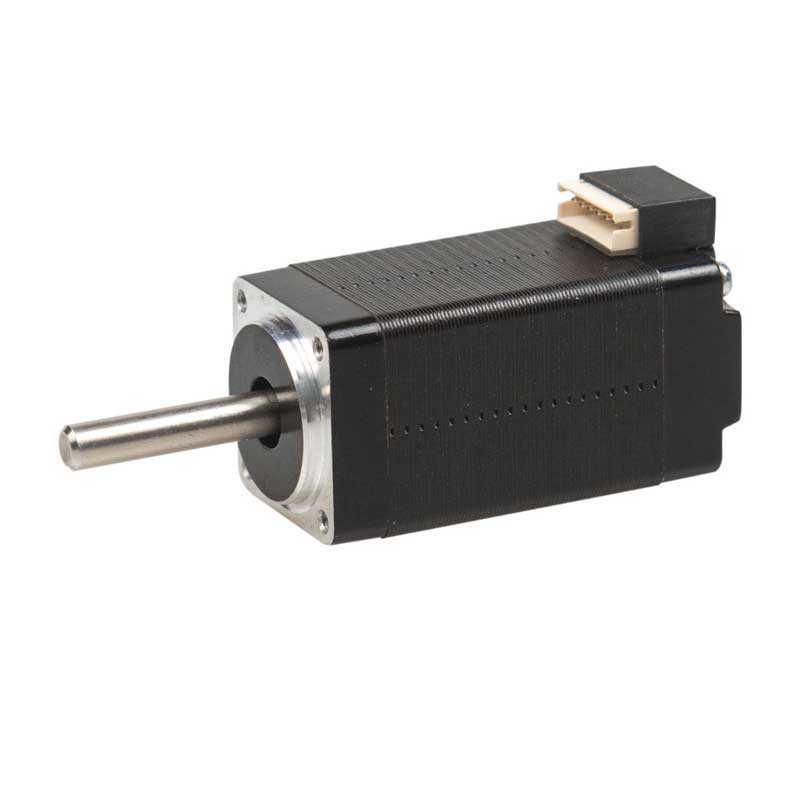

A Hybrid Stepper Motor is a combination of a permanent magnet and a variable reluctance motor. It combines the advantages of both to achieve precise control and high torque output. The operation of a Hybrid Stepper Motor is based on the interaction between the stator and the rotor. The stator consists of two or three windings arranged around the motor, while the rotor has permanent magnets and teeth. As current flows through the windings, it generates a magnetic field that drives the rotor by aligning with the stator's magnetic field.
The main differences between two-phase and three-phase Hybrid Stepper Motors are as follows.
1. The number of windings used and the control signal.
Two-phase stepper motors use two stator windings that are alternately energized to rotate the rotor by attracting and repelling each other. In contrast, three-phase stepper motors use three stator windings that are energized sequentially, causing the rotor to rotate multiple steps per revolution.
Two-phase and stepper motor 3 phase offers a variety of advantages over other motor types. For example, they offer high accuracy and precision, low cost, and the ability to operate in an open-loop control system. In addition, they have better torque and speed characteristics than brushed DC motors or AC induction motors.
(1) Two-phase Hybrid Stepper Motors are typically used for low to medium torque applications that require high accuracy. They are also used in applications where the system requires simple control and the complexity of the motor is not an important issue. Two-phase Hybrid Stepper Motors are also common in simple industrial applications, such as printers, scanners and robots.
(2) 3 phase stepper motors are used for higher torque applications due to their more robust and efficient design. These motors are also used in applications where the system requires better resolution and high-speed performance. Three-phase Hybrid Stepper Motors are typically used in industrial applications such as CNC machines, automation and robotics.
2. Cost.
Typically, two-phase stepper motors are cheaper than three-phase stepper motors. This is because two-phase Hybrid Stepper Motors have less wiring, less control electronics, and simpler construction.
In contrast, three-phase Hybrid Stepper Motors are more complex and require more components, including more wiring and better control electronics. This complexity results in higher manufacturing costs, making three-phase Hybrid Stepper Motors more expensive. However, their higher performance, efficiency and durability justify their higher cost.
In summary, the choice between two-phase and three-phase Hybrid Stepper Motors depends on the specific requirements of the application. For low-torque and low-speed applications, a two-phase stepper motor may be more appropriate, while higher-torque and high-speed applications may require a three-phase Hybrid Stepper Motor. System complexity, resolution and cost are also factors to consider when choosing between the two. Overall, Hybrid Stepper Motors are a robust, reliable and efficient choice for many electromechanical systems. If you need more detailed information, please feel free to contact us!